Proudly Part of Privia Health
PAE For An Enlarged Prostate
Prostate Artery Embolization for An Enlarged Prostate (BPH)
Problem Solving
- What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
- What are the symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
- How common is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
- How is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia diagnosed?
- What are the incidence and risk factors for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Prioritize Counseling
- What if I ignore the symptoms of Benign Prostatic hyperplasia? What are the complications of Benign prostate hyperplasia?
- How Benign Prostate Hyperplasia is treated?
- What is a Prostate embolization or Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
- Is Prostate artery embolization (PAE), a minimally invasive procedure?
- Who is a good candidate for Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
- How should I prepare before the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
- How does Dr. Patel (Interventional Radiologist (IR)) treat Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia? How Prostate artery embolization procedure performed?
- How long does the Prostate artery embolization procedure takes?
- What recovery looks like after Prostate artery embolization?
- What kind of follow-up care is typical after Prostate artery embolization?
Patient Safety
- Is Prostate artery embolization safe? What are the side effects of Prostate artery embolization?
- Foley catheter after Prostate artery embolization?
- What are the common complications that are specifically related to TURP/Open surgery but not with PAE?
- Is Prostate artery embolization better than Surgical options? Is Prostate artery embolization better than TURP?
Personalized Care
- Have other treatments failed, leading you to believe surgery is the only option left?
- Are You Dreading surgical treatment options?
- What are the different treatment options available?
- What are some unique advantages of Prostate artery embolization (PAE) as compared to other surgical options?
- Who is a good candidate for Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
- When Prostate artery embolization is a superior treatment option? And How come I haven’t heard about the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
- What are other indications for the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
- How can benign prostatic hyperplasia be prevented?
Quality Of Life
- Does an enlarged prostate limit your quality of your life? Are you a candidate?
- What is the ultimate Goal?
Problem Solving
What is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
In layman’s terms, Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia = Big Prostate. And it is not the same as prostate cancer.
The prostate is a walnut-shaped gland that is part of the male reproductive system. The main function of the prostate is to make a fluid that goes into semen. Prostate fluid is essential for a man’s fertility.
The prostate is located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum and surrounds the urethra (the tube that empties urine from the bladder).

What are the symptoms of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)?
The prostate goes through two main growth periods as a man ages. The first occurs early in puberty when the prostate doubles in size. The second phase of growth begins around age 25 and continues during most of a man’s life. Benign prostatic hyperplasia often occurs with the second growth phase.
This can cause the urethra to narrow and reduce urine flow. For some men, the reduction in the flow of urine can be significant. Some symptoms include:
- Frequent and at times urgent need to urinate
- Increased frequency of urination at night
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
More severe symptoms include:
- Urinary tract infections
- Inability to urinate – Acute urinary retention
- Blood in the urine
How common is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Very common.
About half of men between 51 and 60 develop the condition, and that number steadily climbs in the decades that follow. And up to 90 percent of men older than 80.
How is Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia diagnosed?
To diagnose BPH, Dr. Patel evaluates a patient’s medical history, performs a physical exam, and runs diagnostic tests.
As a first step, Dr. Patel will collect information about the patient’s medical history. Typically questions center on urinary symptoms associated with BPH including urination frequency, nighttime urination habits, the feeling of incomplete bladder emptying and urgency to urinate, and whether the patient needs to strain to urinate. Dr. Patel may also ask about daily fluid intake, consumption of caffeine and alcohol, and whether the patient takes medications that can affect urination.
In most cases, Dr. Patel will order some additional tests to help confirm a diagnosis of BPH, including bloodwork to measure the levels of prostate-specific antigen (PSA), a protein produced by the prostate gland. Elevated levels of PSA may be a sign of an enlarged prostate.
A urinalysis, a test in which a patient urinates into a container, is sometimes recommended. This test checks for signs of a urinary tract infection, blood in the urine (hematuria), and kidney function.
Dr. Patel may also recommend other tests that measure the rate of urine flow and the amount of urine that remains in the bladder after urination. Dr. Patel will also order an ultrasound of the prostate and/or a cystoscopy, a procedure in which a cystoscope—a tube equipped with a small lens—is inserted into the urethra to allow the doctor to examine the urethra and bladder.
What are the incidence and risk factors for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia?
Several risk factors increase the chances that a man will develop BPH:
- Age. BPH is often considered a normal part of aging. The risk for BPH increases as men get older. A majority of men over the age of 50 have one thing in common: an enlarged prostate.
- Family history.
- Metabolic Syndrome and obesity. Some evidence suggests that men who are obese or who have metabolic syndrome or hormonal (Estrogen) related are at increased risk for developing BPH.
- DM, Heart disease, Erectile dysfunction.
Prioritize Counseling, Information is the key.
What if I ignore the symptoms of Benign Prostatic hyperplasia? What are the complications of Benign prostate hyperplasia?
You will be at risk of complications such as
- acute urinary retention
- chronic, or long-lasting, urinary retention
- blood in the urine
- Urinary tract infection (UTI)
- bladder damage
- kidney damage
- bladder stones
How benign prostatic hyperplasia is treated?
Treatment options for benign prostatic hyperplasia may include
- lifestyle changes
- Medications
- Minimally invasive procedures
- More invasive surgery
A health care provider treats benign prostatic hyperplasia based on the severity of symptoms, how much the symptoms affect a man’s daily life, and a man’s preferences.
Men may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless their symptoms are bothersome and affect their quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, a urologist may recommend regular checkups. If benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms become bothersome or present a health risk, a urologist most often recommends treatment.
What is a Prostate embolization or Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
This is a cutting-edge, innovative procedure directed towards decreasing size to the prostate via reducing the blood supply to the prostate covering urethra (Bladder outflow) which in turn allow urination, reduces pain and foley dependence related to retention.
Is Prostate artery embolization (PAE), a minimally invasive procedure?
Yes. Unlike invasive surgery, Dr. Patel, an experienced Interventional Radiologist, performs an image-guided outpatient procedure avoiding surgery while preserving your uterus & ovaries, controlling symptoms, and significantly improving your quality of life. Isn’t this amazing? Approximately 9 out of 10 women who undergo uterine fibroid embolization will experience significant symptomatic fibroids improvement.
Who is a good candidate for Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
PAE is a non-surgical treatment alternative for men with severe BPH who have failed medical therapy and who do not wish to undergo or are ineligible for surgery.
PAE can help elderly patients with large prostates with high resection volume and can provide an effective alternative to conventional surgery.
Dr. Patel will meet with you to review your medical history and imaging studies. Together, we will determine whether PAE is right for you.
How should I prepare before the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
Some medications should be stopped or reduced – you should discuss your medications with your doctor. You should fast for at least 6 hours before the procedure, though water can be taken with your normal medications. Before the intervention, you will receive some antibiotics to prevent infection.
How does Dr. Patel (Interventional Radiologist (IR)) treat Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia? How Prostate artery embolization procedure performed?
The excessive Prostatic growth reduces the quality of life for many men as it ‘pinches’ the urethra and prevents complete emptying of the bladder, resulting in the need to pass urine very frequently, including during the night, disturbing sleep. The purpose of prostatic artery embolization (PAE) is to limit the symptoms of BPH by reducing the blood supply to the prostate gland, causing it to shrink.
Under X-ray guidance and sedation, Dr. Patel will access the artery through a small incision in the wrist or groin. Dr. Patel then guides a very thin catheter (about the size of a strand of spaghetti) into the incision and through your blood vessels to the Prostatic artery.
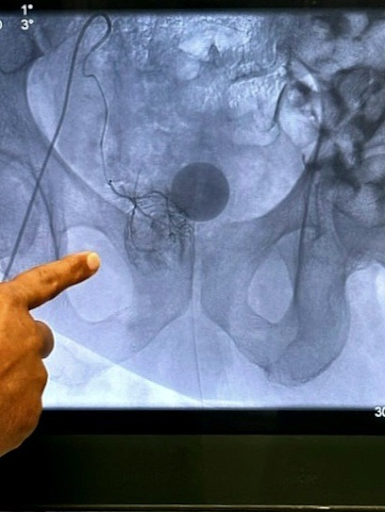
Once the catheter is in the proper position, the doctor releases small particles (like tiny sand granules) at the targeted location to block the small vessels and deprive the prostate of nutrients. Prostate artery embolization is performed in both Prostatic arteries. At the completion of the embolization procedure, pressure is applied to the small incision to allow it to heal.
Outpatient Procedure, you’ll be sent home with oral pain medication to use for an additional few day.
How long does the Prostate artery embolization procedure takes?
This outpatient procedure takes around 1-3 hours and the patient will return home later that day. Procedures may take between 1 and 3 hours depending on how the prostatic veins are located or are large. The PAE procedure blocks blood flow in the regions of the prostate most vulnerable to BPH and causes death in isolated areas.
What recovery looks like after Prostate artery embolization?
Immediately after embolization, your prostate will no more have blood to supply it so it shrinks to smaller dimensions. The bladder outflow opens, and thus able to empty more efficiently.
Many men are able to resume their normal daily activities within 3 days of their procedure.
In most cases, relief begins to occur within a week, as the prostate starts to shrink, relieving the pressure on the urethra and improving lower urinary tract symptoms.
What kind of follow-up care is typical after Prostate artery embolization?
Patient follow-ups are 2 weeks, 2 months, 6 months, and 1 year after the procedure.
PATIENT SAFETY is the Paramount goal.
Is Prostate artery embolization safe? What are the side effects of Prostate artery embolization?
Much less frequent & less severe than invasive surgery.
Risks include but are not limited to temporary urinary retention, Perineal pain, Infections of the prostate and Bladder, and Irreparable damage to an artery. A collection of blood beneath a skin surface (hematomas) on a punctured area of the groin. Most of them are self-limited and easily manageable. Rare complication of any invasive procedure, Death can occur, however PAE is the safest procedure as compared to any other surgical option. That means more severe complication likely to occur with other surgical options as compared to PAE.
Foley catheter after Prostate artery embolization?
A catheter is used for urination. If you are already foley dependent then expect to have it removed in a follow-up(1-2 weeks) visit. Patients who had no previous dependency on a catheter usually be withdrawn shortly after their PAE procedures. In small cases, you may leave home with a Foley catheter, which will be removed in a follow-up appointment.
What are the common complications that are specifically related to TURP/Open surgery but not with PAE?
Retrograde ejaculation is the most common long-term complication of TURP and can occur in as many as 65 to 75% of men. This is where semen doesn’t come out of your penis during sex or masturbation, but flows into your bladder instead.
Up to 10% of men who have a TURP have difficulty getting and maintaining an Erectile dysfunction afterwards. This can be either temporary or permanent.
Some degree of urinary incontinence, where you pee without meaning to, is quite common after TURP.
Persistent bleeding during or after the operation, urinary tract infection (UTI) & Acute urinary retention are also common after TURP and Open surgery.
TURP syndrome: A rare but potentially serious risk associated with a TURP is known as TURP syndrome. This occurs when too much of the fluid used to wash the area around the prostate during the procedure is absorbed into the bloodstream. Initial symptoms of TURP syndrome include: feeling or being sick, confusion, dizziness, headache, swelling of your tummy, slow heartbeat, left untreated, life-threatening problems can develop, such as seizures or fits, shortness of breath, blue skin (cyanosis) and coma.
The potential benefits of prostate artery embolization compared with surgery are fewer complications, faster recovery and you can have this procedure as an outpatient.
Is Prostate artery embolization better than Surgical options? Is Prostate artery embolization better than TURP?
PAE is a newer, faster, safer, minimally invasive treatment and an easier way to relieve the symptoms caused by BPH. As compared to various surgical options (Transurethral resection (TURP, TUIP), Open prostatectomy), PAE patients had a significantly more pronounced mean decrease in prostate size resulting in several benefits. An outpatient procedure, Shorter Recovery time, Low risk of sexual side effects, low risk of urinary incontinence, no retrograde ejaculation, no indwelling foley catheter, and decrease pain and discomforts.
Personalized Care
Have other treatments failed, leading you to believe surgery is the only option left?
Know the evidence, Proven Efficacy & Avoid the Hospital.
Are You Dreading surgical treatment options?
There are plenty of reasons to be hesitant or skeptical. Our only goal is to help you to make an informed decision regarding your care in Personalized manner.
What are the different treatment options available?
Options are:
Conservative: Life style modifications, Medications, Foley dependent life
Minimal Invasive: Prostate Artery Embolization
More Invasive to an Open surgery:
- TURP / TUIP: Transurethral resection
- Open prostatectomy
Men may not need treatment for a mildly enlarged prostate unless their symptoms are bothersome and affect their quality of life. In these cases, instead of treatment, a urologist may recommend regular checkups. If benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms become bothersome or present a health risk, a urologist most often recommends treatment.
What are some unique advantages of Prostate artery embolization (PAE) as compared to other surgical options?
PAE is
- Versatile: Most patient will benefit
- Succeeds when other technique fails: large prostate and large median lobe
- Sexual Function: Often improves with preserved fertility
- Can Discontinue medical therapy
- Very strong safety Profile
- Outpatient Minimal invasive procedure
- Does not preclude surgery later
Who is a good candidate for Prostate artery embolization (PAE)?
PAE is a non-surgical treatment alternative for men with severe BPH who have failed medical therapy and who do not wish to undergo or are ineligible for surgery.
PAE can help elderly patients with large prostates with high resection volume and can provide an effective alternative to conventional surgery.
Dr. Patel will meet with you to review your medical history and imaging studies. Together, we will determine whether PAE is right for you.
When Prostate artery embolization is a superior treatment option? And how come I haven’t heard about the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
You are not alone.
Unfortunately, this technique is unique, difficult to reproducible in term of outcomes and safety, that has not been popularized yet require additional skillset and only available at few novel centers of excellence.
Due to a lack of knowledge, most of the patients either receive conservative therapy, physical therapy, or total Knee replacement surgery.
Given Dr. Patel’s far-reaching knowledge, approach and experience, this is now offered in Space Coast area.
What are other indications for the Prostate artery embolization procedure?
Apart from the most common indication for Benign prostatic hyperplasia, is indicated in Prostate cancer for symptom relief, Hematuria (blood in urine) from the Prostate origin, etc.
How can benign prostatic hyperplasia be prevented?
Researchers have not found a way to prevent benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Quality Of Life
Does an enlarged prostate limit your quality of your life? Are you a Candidate?
- Do you avoid activities because of Frequent & Urgency and strain related to urination?
- Does frequent bathroom visit disturb your sleep?
- Is your life foley dependent?
- Do you frequently suffer from Urinary tract infections?
- Do you worry about sexual dysfunctions from urology surgery?
- Do you want avoid or not a candidate or dreading about Total Knee Replacement?
If any of above is true, then We can help you improve your Quality of Life! We NEVER do surgery and can show you options that can work for you.
What is the ultimate Goal?
An ultimate goal for DR. Patel is that an impact of any and all medical interventions significantly improves overall well-being, including physical, emotional, social, and psychological aspects of their quality of life without compromising patient safety.
