Proudly Part of Privia Health
Audiology
Our audiologist, Dr. Wilson is highly trained in the diagnosis and treatment of hearing loss and other ear-related disorders. Using the latest technology available, they work closely with our physicians to help patients of all age ranges.

Diagnostics
Audiogram
Typically a human ear hears a range of sounds from 20 Hertz (Hz) to 20,000 Hz. That being said, most speech and ambient sounds are concentrated between 250 Hz and 8,000 Hz. An audiogram assesses the softest/quietest level at which you can hear tones within this frequency range. You will also be asked to repeat words to determine how well you understand speech at a comfortable volume level. On average, this test usually takes about 10-15 minutes. In children under the age of 6 (and even as young as 6 months, on occasion), a system of lights, toys, and screens are used instead of headphones to help determine the hearing levels in each ear.
Tympanogram
The middle ear, or the space behind the eardrum, is connected to the back of the nose by the Eustachian tube. Certain conditions such as allergies, upper respiratory infections, or ear infections can cause a buildup of pressure behind the eardrum, which can cause a blocked or full sensation in the ear. This can also frequently cause hearing loss as well. A tympanogram is a quick (30 seconds or less) and painless test that measures the movement of the eardrum in response to a small puff of air into the ear canal. If the eardrum movement is impaired, this can be an indication of something amiss in the middle ear space.
Auditory brainstem response (ABR)
In certain cases where a patient has asymmetric hearing loss (that is, one ear hears better/worse than the other), an ABR test can help figure out where along the auditory pathway the problem lies, from the cochlea all the way to the brainstem. Typically, this test involves the placement of a series of adhesive electrodes to the scalp to measure the speed of the nerve signal from the ear to the brain. This test does take longer than a regular audiogram, sometimes up to 30-45 minutes.
Videonystamography (VNG)
A VNG is actually a battery of several different tests, all of which help to diagnose vertigo and balance disorders related to the inner ear. This test involves moving the head and body into different positions, as well as stimulating both ears with cool and warm air. Special goggles are worn by the patient during these maneuvers, which are connected to software that track eye movements. These eye movements are then quantified to determine if the inner ear’s balance (vestibular) system is malfunctioning. It is not unusual for patients to experience momentary dizziness during this test, but it is not uncommon to have a period of unsteadiness for several hours after the test. A VNG usually takes about 1 hour to complete.
If you are scheduled for a VNG, please note the following:
- Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking for 3 hours before testing.
- Do not wear eye make-up (mascara, eye shadow, eye liner).
- Avoid drinking any alcoholic beverages for 48 hours prior to testing.
- Do not take any sedating medications (e.g Benadryl), muscle relaxants (e.g Flexeril, Valium), and sleep aids (e.g Unisom, Ambien) for 48 hours before testing.
- Avoid taking any anti-vertigo (e.g meclizine) or anti-nausea (e.g Zofran, Compazine) medications for 48 hours before testing.
- Make sure that you have someone who can take you home afterwards (preferably a friend or relative, rather than an Uber or Lyft).
Hearing Aids
- Hearing aids are commonly used by patients with irreversible or longstanding hearing loss. They can also help significantly with tinnitus (ringing in the ears), especially in patients who also have concurrent hearing loss. Hearing amplification of any sort (including hearing aids) is crucial to the rehabilitation process of the portions of the brain that process sound. The less stimulation those portions of our brains receive from our ears, the more likely they are to slowly shut down over time (the common adage of “if you don’t use it, you lose it” definitely applies here!). Therefore, we strongly encourage hearing aids for even mild to moderate hearing loss, so as to prevent future difficulty understanding speech or other ambient sounds such as music. From a tinnitus standpoint, prolonged hearing aid use has been shown to significantly reduce or completely eliminate it altogether.
- Modern hearing aid technology has advanced significantly even in the 21st century. The vast majority of devices have wireless connectivity via Bluetooth, which allows for hands-free connection to devices such as smartphones, car stereos, and televisions. Many devices also have different pre-made settings that are managed via a physical switch, or wirelessly with a smartphone app. These settings can adjust the hearing aid sensitivity “on the fly” for specific environments such as restaurants and concerts. Your audiologist can help determine which hearing aid is right for you with respect to both your lifestyle as well as your degree of hearing loss.
- Why choose hearing aids with us?
- Big box and other similar stores usually offer hearing aids at a lower price, but at the cost of fewer features and support services. They also usually charge a separate fee for adjustments and device repairs. At ENT & Facial Plastic Surgery, we always provide a free hearing aid demonstration to all potential hearing candidates. This means you can take your hearing aid(s) home with you, free of charge, to try at home (or in restaurants, concerts, etc.) for a week. Only when you bring them back after the trial period do you have to make a decision on whether or not to purchase them. Furthermore, hearing aids purchased through our office are covered with a 1-year warranty, and future adjustments are completely free of charge. We also offer a protection plan for lost or damaged devices with a low deductible. Lastly, if you ever have any medical issues related to your ears, such as impacted ear wax or an ear infection, you can usually see one of our physicians to have that addressed without having to make a second appointment.
- In-ear hearing aids
-
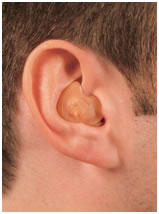
Hearing aids of this style are custom made for the shape of individual ear canals for better comfort. The custom hearing aids can be very small and fit deeper in the ear, rendering them virtually invisible. These hearing aids are suitable for a mild to moderate hearing loss.
-
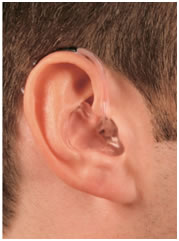
- Behind-the-ear hearing aids
-
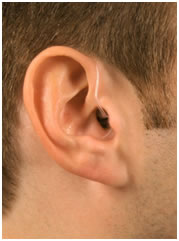
Hearing aids of this style sit behind the ear and are suitable for all ranges of hearing loss. These devices come in a variety of different colors to match your skin or hair color, so you should never feel self-conscious about your hearing aids.
-
- We currently offer a full catalogue of hearing aids manufactured by Oticon, Phonak, and Resound.
- Please note that most insurances do not cover hearing aids, although some types of insurance may cover up to a certain amount for hearing aids every 3-5 years. Our audiologists and billing staff can help check that for you at the time of your visit. We do offer more traditional payment plans through Care Credit.
Implantable Hearing Devices
- There are certain situations where a traditional hearing aid is either not feasible (due to anatomic concerns such as lack of an ear canal, or damage to the eardrum/middle ear bones) or insufficiently powered to help with severe hearing loss. In these cases, a surgically implanted hearing device may be the best way to restore your hearing.
- Bone-anchored hearing aids
- Conductive hearing loss is a specific type of hearing loss that primarily affects the ear canal, the eardrum, and the small hearing bones behind the eardrum (ossicles). Issues along this pathway cause hearing loss due to lack of sound waves vibrating into the inner ear. In cases where the hearing loss is not amenable to surgery (such as eardrum repair or replacement of the ossicles with a prosthesis), a bone anchored hearing aid is a possible solution. This type of hearing device has two parts, an internal implant, and an external processor. The implant is fixed to the bone of the skull behind the ear as an outpatient procedure. After allowing a few weeks for adequate healing of the area, a magnetic processor on the outside is attached. The processor has a microphone that captures ambient sound waves and wirelessly transmits it to the internal device. The internal device then vibrates the bone directly to transmit sound to the inner ear, therefore bypassing any potential blockage in the ear canal or middle ear space.
- Cochlear implants
- Patients with severe hearing loss, especially those who fail to derive any benefit from traditional hearing aids, may be eligible for a cochlear implant. The implant has two parts, an internal implant/electrode and an external processor. The implant is placed on top of the bone of the skull behind the ear. A small opening is then created through the bone behind the ear (mastoid bone), and the electrode is implanted directly into the inner ear (cochlea). This is typically an outpatient procedure (even for children). After allowing a few weeks for adequate healing of the area, a magnetic processor on the outside is attached, and the internal implant is then activated. The processor has a microphone that captures ambient sound waves and wirelessly transmits it to the internal device. The internal device then converts that sound to electrical signals along the electrode, which is then interpreted by the brain as sound. Patients typically take a few months of auditory
Ear Molds & Hearing Protection
Practicing good hearing conservation is the best way to protect your ears when in noisy environments. These are commonly encountered from your workplace (construction equipment, factory machinery, firearms) to your personal life (concerts, loud snoring). Please talk to our audiologists about ordering some custom-made filtered ear plugs if you often find yourself needing to tune down the ambient noise. We also make custom swim molds to protect your middle ears from water if you have an eardrum perforation or ear tubes.
Tinnitus
Tinnitus, or ringing in the ear(s), is a condition that affects up to 10-15% of adults in the US alone. At best, it is an annoyance, and at worst, it is a debilitating condition that can interfere with sleep quality, as well as overall quality of life. Most commonly, patients with tinnitus suffer from some degree of hearing loss. The brain “makes up” sounds to replace the lost input at the affected frequencies. Once the hearing is restored, the tinnitus is either dramatically reduced over time, or goes away completely. Tinnitus can also be associated with stress and anxiety, which can frequently manifest as teeth grinding (bruxism) and inflammation of the jaw joint (TMJ disease). Whatever the cause of your tinnitus, you can expect to have a full hearing test at your appointment.
How to Treat Tinnitus
- Hearing aids/implantable hearing devices
- Hearing restoration has been clinically proven to reduce tinnitus over time. The key is diligent use of the hearing aid or device to “train” the brain to accept input at the lost frequencies again.
- White noise therapies
- Putting on some form of background noise (TV, music, etc.), especially in quiet environments (studying, working, sleeping), can help to “distract” the ear(s). This can help reduce one’s awareness of the tinnitus, although it does not necessarily treat the tinnitus directly.
- Masking devices
- A masker device is similar to a hearing aid, but instead of amplifying all ambient sounds, it specifically produces a white noise pattern that “cancels out” the tinnitus. This may be different for each patient, and can be adjusted accordingly. Please speak to your audiologist about whether this might be a viable option for your tinnitus.
Balance & Dizziness
What exactly is vertigo? Is it the same as dizziness?
True vertigo is a disorder of the inner ear, and is characterized by the sensation of room spinning, even though your head or body may be completely still. Dizziness is a more general term that describes any disruption in one’s sensation of balance or equilibrium. Vertigo is just one type of dizziness. There are a myriad of other non-ear causes for dizziness, such as low blood pressure, migraines, heart conditions, asymmetric hearing loss, neck/spine issues, etc. Your ENT and audiologist can help determine what is causing your dizziness.
Epley maneuver
Benign positional vertigo is a common condition that is characterized by brief, episodic vertigo lasting less than 60 seconds. Usually, symptoms are triggered by specific head movements in a certain direction. This can dislodge small crystals in the vestibular system (the balance portion of our inner ears), which can inadvertently trigger nerve receptors that move our eyes to help track objects during rapid head movements. This is usually diagnosed by a medical professional, such as an ENT. The most common therapy for treating this condition is the Epley maneuver. Your audiologist can help perform this with you in our office, as well as provide you with materials to do this maneuver at home if symptoms should ever recur.
Balance therapy/vestibular rehab
Physical therapy can be a very useful treatment modality for people with balance issues, regardless of whether they are due to an inner ear problem or not. Vestibular rehabilitation, or balance therapy, is a form of physical therapy that trains the brain as well as the body to desensitize to dizzy symptoms, as well as minimize their effect. This is accomplished using a combination of anticipatory techniques, gait coordination training, and reducing dependency on visual inputs. Your ENT physician will discuss this in more detail with you, if this is a viable treatment option.