-
Patient Information
-
-
Patient Information
-
-
Services
-
Proudly Part of Privia Health
Thyroid Ultrasound
Ultrasound Examination
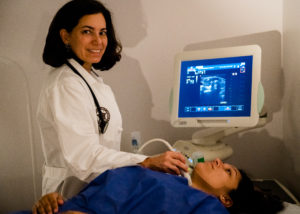
Ultrasound examination is the most accurate and useful imaging test to detect nodules or lumps within the thyroid gland. Ultrasound procedure uses sound waves to produce images of the thyroid gland and the images can be captured to assess the size, shape, structure and any abnormalities of the thyroid gland. Accurate measurement of the size of the thyroid nodules can be made using ultrasound imaging. It also assists in evaluation of the variations in the thyroid tissue such as enlargement caused by goiter and decrease in size caused by inflammation, and can differentiate between solid, fluid filled or complex type of thyroid nodules.
Thyroid ultrasound is recommended by your doctor in following conditions:
- If a thyroid nodule can be felt on physical examination
- In suspicion of hormonal disorder of the thyroid gland
- In swallowing disorders
- If you are at a high risk for thyroid cancer with family history of thyroid malignancy and radiation therapy to the neck during childhood
- To evaluate changes in the size of thyroid nodule during follow-up
- To monitor your condition after surgery for removal of thyroid gland
The role of ultrasound in diagnosis of thyroid conditions is complex and involves detection of the thyroid and neck masses, distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules, and guidance during fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy and percutaneous treatment.
Procedure
You will be made to lie down on your back on the examination table. Your neck should be in extended position so that ultrasound transducer can be placed properly. A gel will be applied to the skin to facilitate conduction of sound waves. The sound waves directed from the transducer are reflected back by thyroid gland structures and these reflected sound waves or echoes are received again by the transducer. The computer analyzes this information and creates several images each second that get displayed on the monitor. The entire procedure may last for about 10 minutes.
Ultrasound of thyroid is a very safe procedure and there is no exposure to radiation as no X-rays or other harmful radiations are not employed in the procedure.
